What’s Happening?
- Create a Special File:
- You need a file called
ft_point.h.
- You need a file called
- Add Some Important Stuff:
- This file will help your program understand what a
t_pointis. Think oft_pointlike a special box that can hold two numbers,xandy.
- This file will help your program understand what a
- Magic Code Explanation:
#ifndef FT_POINT_H: This checks if we have not already included this special file.#define FT_POINT_H: If we haven’t included it, this line says “let’s include it now”.typedef struct s_point: We are creating a new special box calleds_pointthat holds two numbers,xandy.int x; int y;: These are the two numbers inside the box.} t_point;: Now, we give our special box a nickname:t_point.#endif: This ends our check. If we already included the file before, we skip everything between#ifndefand#endif.
What to Put in the File:
Your ft_point.h file should look like this:
#ifndef FT_POINT_H
#define FT_POINT_H
typedef struct s_point
{
int x;
int y;
} t_point;
#endif
What It Does:
- Check and Include: It checks if the file has been included before and includes it if not.
- Create a Box: It makes a special box (
t_point) to hold two numbers (xandy).
Main Program:
In your main program:
#include "ft_point.h"
void set_point(t_point *point)
{
point->x = 42;
point->y = 21;
}
int main(void)
{
t_point point;
set_point(&point);
return (0);
}
This program will:
- Use the Special Box: Include the file that defines the special box
t_point. - Set Values: Put the numbers
42and21intoxandyof the special box. - Run the Program: Create a
pointand set itsxandyvalues using theset_pointfunction.
That’s it! Now you have a file that helps your program understand and use a special box called t_point to store two numbers.
| Name | File Image |
|---|---|
| ft_point.h | 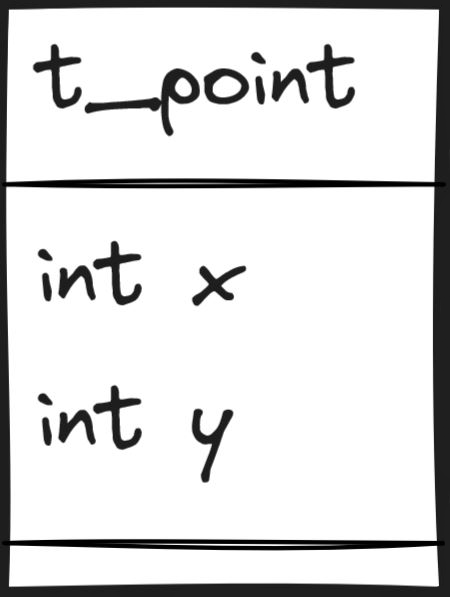 |
| main.c | 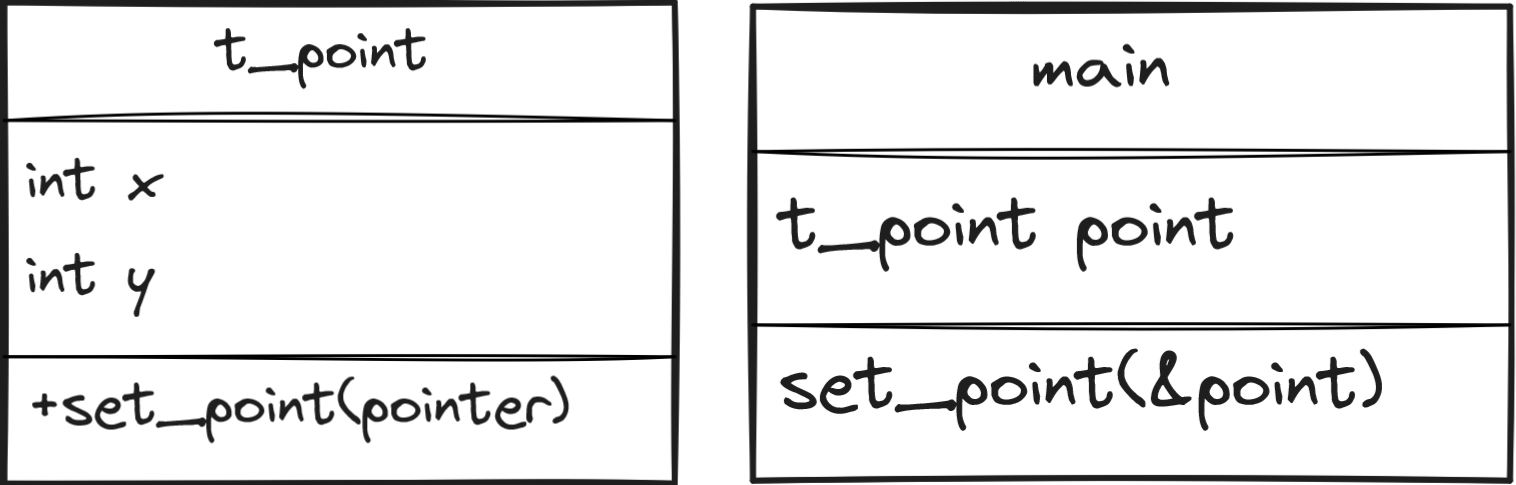 |